Welcome to Cloud Computing for Beginners, a comprehensive guide designed to demystify the world of cloud computing. In this blog post, we will break down complex cloud concepts and provide you with a clear understanding of the fundamental principles behind this transformative technology.
Whether you’re a seasoned tech enthusiast looking to deepen your knowledge or a curious beginner eager to explore the possibilities, this blog post will serve as your entry point into the captivating realm of the cloud. So, let’s embark on this educational journey together and unravel the mysteries of the cloud.
What is “Cloud Computing”?
Cloud Computing refers to a remote server network that stores, manages, and processes data, allowing users to access and utilise resources and services over the Internet rather than relying on local infrastructure. It offers scalable, on-demand computing power, storage capabilities, and software applications, enabling organisations and individuals to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and reduce costs. The cloud provides a flexible and efficient solution for accessing and managing data and applications, independent of specific vendors or platforms.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Cloud Computing works by utilising a distributed network of remote servers. These servers are interconnected and work together to store and process data. When users access the cloud, their requests are sent to these servers over the Internet. The servers then retrieve and deliver the requested data or perform the requested operations. This allows users to access and utilise resources and services on demand without needing local infrastructure or physical storage devices.
The cloud also employs virtualisation technology, enabling efficient allocation and utilisation of computing resources. This means multiple users can share the same physical server while maintaining isolation and security. Additionally, the cloud offers automatic scalability, allowing users to scale their resources up or down based on their needs. This flexibility and elasticity make the cloud ideal for businesses with fluctuating demands or growth aspirations.

Why the Hype Around Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has garnered significant attention and excitement due to its ability to revolutionize how we access and utilize technology resources. Imagine the cloud as a vast network of servers that acts as a virtual storage and computing powerhouse. Like how electricity is delivered to our homes, cloud computing delivers computing power and data storage capabilities directly to users over the internet. This analogy allows individuals and businesses to access and utilize resources on demand without needing local infrastructure or physical storage devices.
Benefits of the Cloud
The cloud offers numerous benefits, making it a game-changer in today’s digital landscape. With the cloud, businesses can enjoy increased scalability, allowing for easy expansion or contraction of resources based on demand. Additionally, the cloud enables seamless collaboration and remote access to data and applications, fostering productivity and flexibility. Moreover, leveraging the cloud eliminates the need for expensive hardware and maintenance costs, resulting in significant cost savings. The cloud empowers organisations to optimise operations, boost efficiency, and drive innovation in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are two key benefits of the cloud. The cloud allows businesses and individuals to scale their computing resources up or down based on their needs without needing expensive hardware investments or infrastructure changes. Additionally, the cloud enables users to access their data and applications from anywhere, on any device, providing the flexibility to work remotely and collaborate seamlessly.
Furthermore, the cloud offers automatic software updates and maintenance, eliminating the hassle of manual updates and ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and enhancements. With its pay-as-you-go pricing model, the cloud optimises cost by only paying for the resources used, avoiding unnecessary expenses. Ultimately, leveraging the cloud empowers businesses to focus on their core competencies and innovation while leaving the technical complexities to the cloud service providers.
Cost Savings
Cost Savings: The cloud provides cost savings compared to traditional data centres due to its pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for upfront infrastructure investments and reducing maintenance and operational costs. Organisations can scale their resources up or down based on demand, optimising their spending and avoiding unnecessary expenses. Additionally, the cloud eliminates the need for physical hardware and the associated maintenance, power, and cooling expenses, resulting in significant cost savings.
Potential Challenges of Cloud Computing
Security: Cloud computing introduces new security concerns as data and applications are stored off-site. Organisations must ensure robust security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Downtime: Dependency on cloud service providers means that any disruptions or outages on their end can impact business operations. Organisations should carefully consider service level agreements (SLAs) and redundancy options to mitigate the risk of downtime and ensure business continuity.
People Skills: Adopting cloud computing requires organizations to develop new skills and capabilities among their workforce. This includes understanding cloud technologies, managing cloud environments, and effectively integrating cloud services into existing workflows and processes.
Costs: While the cloud offers cost savings in many areas, organizations must carefully manage their cloud expenditure to avoid unexpected costs. These can arise from over-provisioning resources, inefficient usage, or lack of visibility into usage patterns. Proper monitoring and governance frameworks are necessary to optimize costs and ensure return on investment.
Ultimately, despite the potential challenges, cloud computing offers significant benefits. Organisations can address these challenges through proactive planning, robust security measures, employee training, and effective cost-management strategies.
Major Cloud Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a primary cloud provider offering many cloud-based services and solutions. As a subsidiary of Amazon, AWS has established itself as a leader in the industry due to its robust infrastructure, scalability, and security features. AWS provides a comprehensive suite of services, including computing power, storage, database management, networking, analytics, and artificial intelligence. With a global presence and a vast customer base, AWS has become a trusted choice for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to leverage the power of the cloud to drive innovation, agility, and cost efficiency.
Microsoft Azure

Microsoft Azure is one of the major cloud providers in the industry. It offers a wide range of cloud services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). As a trusted name in the technology sector, Microsoft brings its extensive experience and expertise to the cloud market. With Azure, businesses can benefit from a robust and secure cloud infrastructure that enables them to build, deploy, and manage applications and services efficiently. Microsoft’s strong commitment to security, compliance, and reliability makes it a preferred choice for organisations seeking a reliable and scalable cloud solution.
Google Cloud Platform

Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Google Cloud Platform is a primary cloud provider that offers a wide range of cloud services and solutions. It is known for its robust infrastructure, scalability, and reliability. GCP provides businesses the tools and resources to build and deploy applications, store and analyse data, and leverage advanced machine learning capabilities. With its global network of data centres, GCP ensures high availability and low latency for businesses operating globally. Overall, GCP’s comprehensive suite of services and its commitment to innovation make it a popular choice for organisations looking to harness the power of the cloud.
What are the cloud service types?
There are three main types of cloud services: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
IaaS provides virtualised computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking capabilities, allowing businesses to build and manage their infrastructure within the cloud environment.
PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It provides a complete development and deployment environment, tools, and services to streamline the application lifecycle.
SaaS delivers software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for organisations to install and maintain software locally. Users can access the applications through web browsers, enabling easy collaboration and seamless device updates.
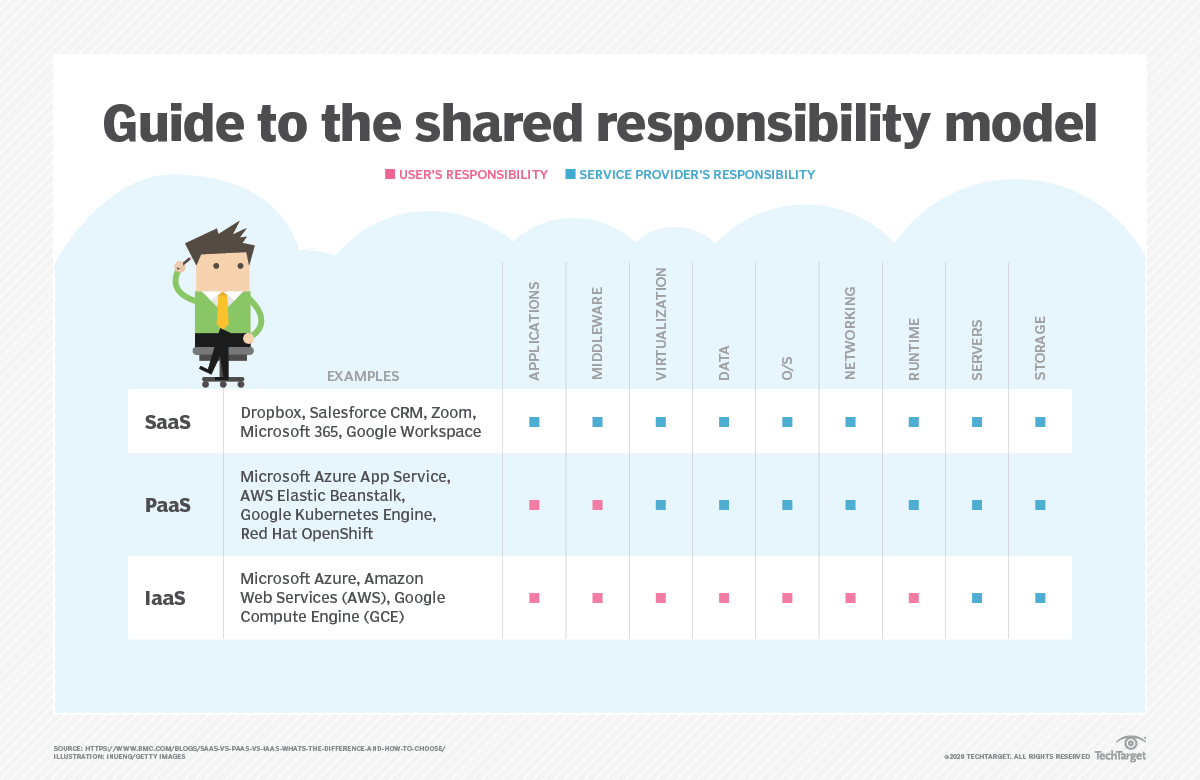
Responsibility in each cloud service type
In IaaS, users manage their applications, operating systems, and data. The cloud provider collects the infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking.
In PaaS, users are responsible for developing and deploying their applications, while the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure and runtime environment.
In SaaS, users are responsible for using the software and data, while the cloud provider handles the application’s maintenance, updates, and security.
Different Types of Cloud Computing
Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud are the three main types of cloud computing.
Public Cloud refers to cloud services provided by a third-party provider over the Internet. It offers scalability and cost-effectiveness, as resources are shared among multiple users.
Private Cloud is dedicated to a single organisation and is hosted either on-premises or by a third-party provider. It provides enhanced security and control but at a higher cost.
Hybrid Cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing organisations to leverage the benefits of both models. It offers flexibility and the ability to customise cloud solutions based on specific needs.
Each cloud type has advantages and considerations, and organisations must carefully evaluate their requirements before choosing the most suitable option.
Pros and Cons of Using Public, Private and Hybrid Cloud
| Cloud Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Scalability and cost-effectiveness | Limited control and security |
| Private Cloud | Enhanced security and control | Higher cost |
| Hybrid Cloud | Flexibility and customization | Complexity in managing two clouds |
When to use Public, Private and Hybrid Cloud
It is essential to consider your organisation’s specific needs and requirements when deciding which cloud type to use. If scalability and cost-effectiveness are your primary concerns, then a public cloud may be the best choice. However, if enhanced security and control are critical, a private cloud would be more suitable despite the higher cost. For those seeking flexibility and customisation, a hybrid cloud can offer the best of both worlds, although managing two clouds can introduce complexity.
What are the benefits of Multi-Cloud Computing?
Additionally, multi-cloud computing allows businesses to avoid vendor lock-in and exploit different cloud providers’ unique features and strengths. It also enhances data security and resilience by spreading data across multiple platforms and locations. With multi-cloud computing, organisations can strategically allocate workloads to the most suitable cloud environment based on specific requirements, such as performance, compliance, and geographical proximity. Ultimately, this approach empowers businesses to maximise the benefits of cloud computing while mitigating risks and ensuring optimal performance for their applications and services.
What are vertical clouds?
Vertical clouds, or vertical cloud computing, refer to deploying cloud resources distributed across multiple data centres or locations. This approach allows for efficient resource utilisation and better scalability, reliability, and performance for applications and services. Vertical clouds enable businesses to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while addressing specific requirements such as data sovereignty, latency reduction, and regulatory compliance. Examples of vertical clouds include healthcare cloud solutions that cater specifically to the needs of the healthcare industry or financial cloud services designed for the financial sector.
Security in cloud computing
Security in cloud computing refers to the measures and mechanisms to protect data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in the cloud. It involves various strategies and practices to ensure the cloud resources’ confidentiality, integrity, availability, and privacy. Some critical aspects of cloud security include:
Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorised access.
Access Control: Implementing proper authentication and authorisation mechanisms to control access to cloud resources.
Network Security: Deploying firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures to protect against unauthorised access and threats.
Regular Audits and Monitoring: Conducting regular security audits, monitoring activities, and analysing logs to identify and respond to security incidents promptly.
Data Backup and Recovery: Implementing robust backup and recovery mechanisms to ensure data can be restored during a security breach or data loss.
Physical Security: Ensuring physical security of data centres where cloud infrastructure is hosted, including restrictions on access, surveillance systems, and environmental controls.
Compliance and Legal Considerations: Adhering to relevant compliance regulations and ensuring cloud service providers comply with applicable data protection laws.
Vulnerability Management: Regularly scanning and patching systems and staying updated with the latest security patches and fixes.
It is important to note that cloud security is a shared responsibility between the cloud service provider and the customer, and both parties need to collaborate to ensure a secure cloud environment.
Further Reading
If you would like to read more about the cloud, please refer to the following articles:
- Coursera Course – Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Getting started with Microsoft Azure
- Getting started with Google Cloud Platform
- Getting started with Amazon AWS
Closing
In conclusion, this beginner’s guide has provided a comprehensive overview of cloud computing, covering its definition, benefits, and critical considerations. By understanding the basics of the cloud, tech enthusiasts, business owners, and professionals can make informed decisions on leveraging this technology for their needs. As you continue your cloud computing journey, I encourage you to follow my social media accounts for more updates and insights. Stay connected and embrace the power of the cloud in your endeavours.
In upcoming articles, I will cover further topics on the cloud journey, starting with a focus on Microsoft Azure data services. Stay tuned.
In the meantime, please feel free to read other articles on this website.
If you want to know about a particular topic, .



